Are you looking for a way to improve your health and reduce your impact on the environment? Are you tired of feeling sluggish and unwell after every meal? Have you been looking for a way to improve your health and reduce your risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes? If so, you might want to consider adopting a plant-based diet. In this blog, we will explore what a plant-based diet is, what foods you can eat on it, what foods to avoid, and the health benefits of this way of eating. Whether you’re a long-time vegetarian or just curious about plant-based diets, this blog will provide you with the information you need to make informed decisions about your diet and health. So, let’s get started!
What is a plant-based diet?
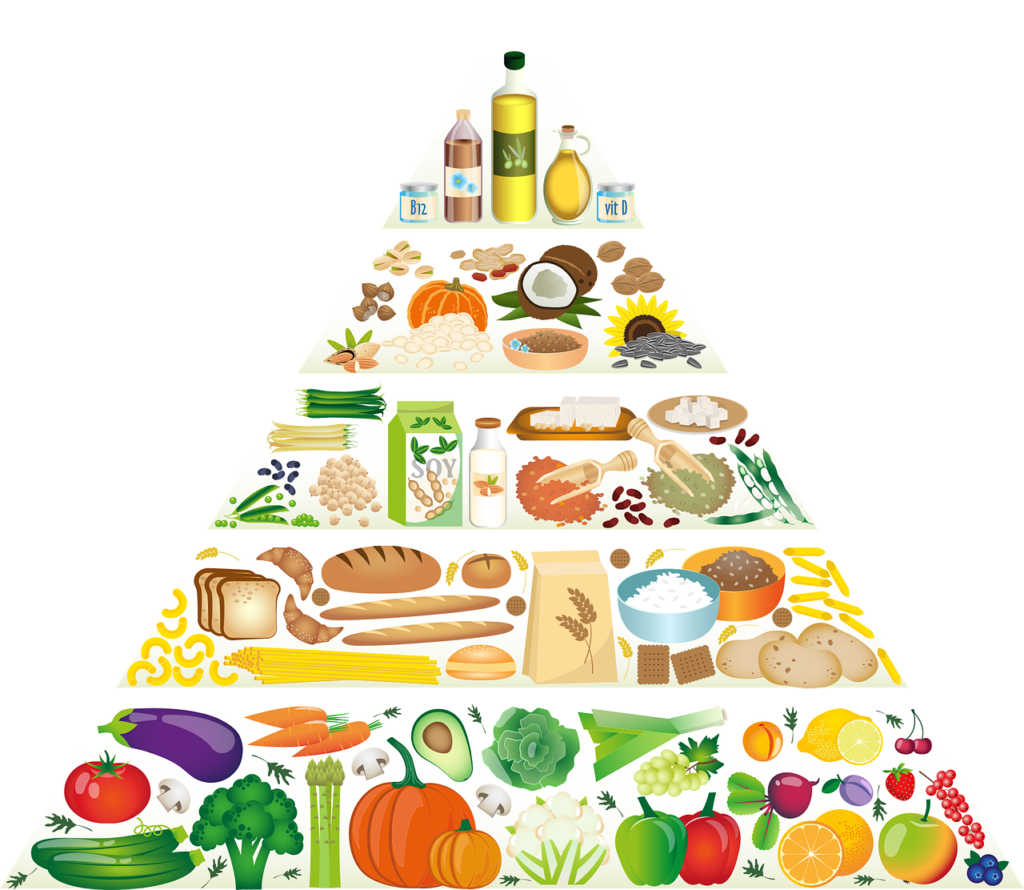
In simple terms, a plant-based diet is one that emphasizes whole, minimally processed foods derived from plants. This includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. While some people who follow a plant-based diet may include small amounts of animal products, such as fish or eggs, the emphasis is on plant foods as the primary source of nutrition.
Why should you try it? What are the advantages and benefits of the plant-based diet?
Health Advantages: Plant-based diets are rich in nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that promote good health. Research has shown that a diet based on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds can lower the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. A plant-based diet is also known to improve digestion, enhance immune function, and promote weight loss.

Environmental Advantages: Animal agriculture is responsible for a significant amount of greenhouse gas emissions, water pollution, and deforestation. By reducing our consumption of animal products and transitioning to a plant-based diet, we can help reduce our environmental impact. Eating more plant-based foods can also conserve water, decrease soil degradation, and reduce the use of fossil fuels.

Economic Advantages: Meat, dairy, and other animal products are often expensive compared to plant-based foods. By eating a plant-based diet, we can save money on grocery bills, reduce healthcare costs by improving our health, and even save money on transportation by reducing the amount of food we import from other countries.

What is the difference between vegan, vegetarian & plant-based diet?
When it comes to diets that focus on plant-based foods, there are several options to choose from, including vegan, vegetarian, and plant-based diets. Vegan and vegetarian diets can be seen as a type or modification of plant based diet. While these diets may seem similar at first glance, there are some key differences that set them apart.
- Vegan diets are the most restrictive of the three, as they exclude all animal-based foods and products. This means no meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, or honey. Vegans often choose this diet for ethical reasons, as they do not want to contribute to the exploitation and mistreatment of animals. However, some vegans may also choose this diet for health reasons or to reduce their environmental impact.
- Vegetarian diets, on the other hand, exclude meat but may include some animal-based products such as dairy, eggs, and honey. There are several types of vegetarian diets, including lacto-ovo vegetarian (which includes dairy and eggs), lacto-vegetarian (which includes dairy but not eggs), and ovo-vegetarian (which includes eggs but not dairy). Vegetarians may choose this diet for ethical, health, or religious reasons.
- Plant-based diets are the most inclusive of the three, as they simply focus on consuming whole, plant-based foods while limiting or avoiding animal-based foods. This can include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. While some plant-based dieters may exclude all animal-based foods, others may include small amounts of animal products such as eggs or dairy. People may choose a plant-based diet for a variety of reasons, including health, environmental, or ethical concerns.
What foods can you eat on a plant-based diet?
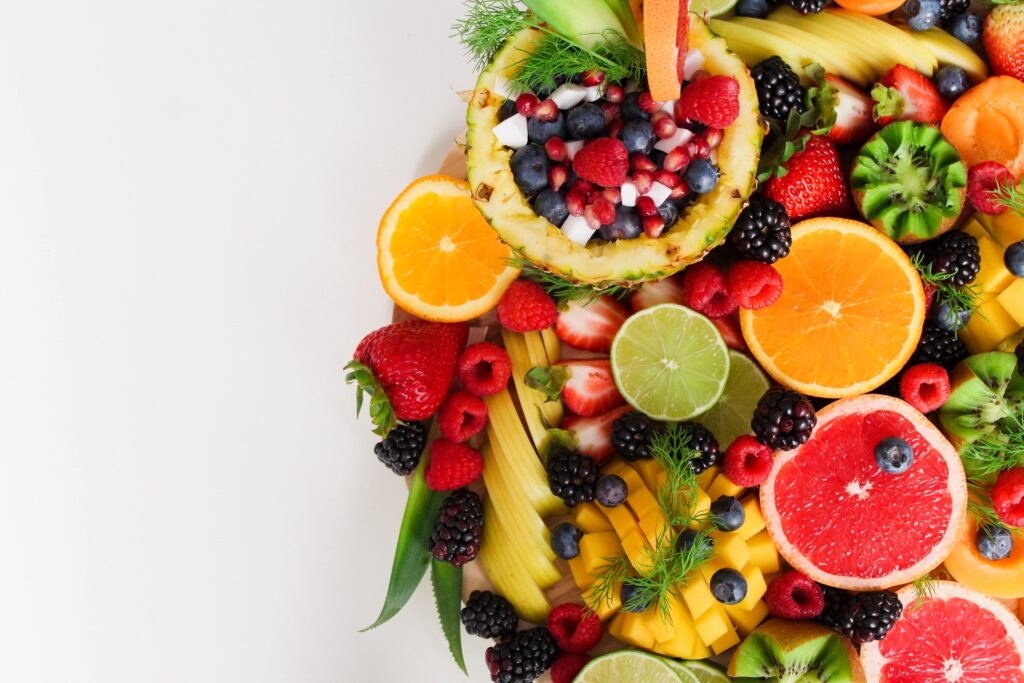

Fruits and Vegetables: These are the cornerstone of a plant-based diet. They provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Be sure to eat a variety of fruits and vegetables in a range of colors to get the full spectrum of nutrients.
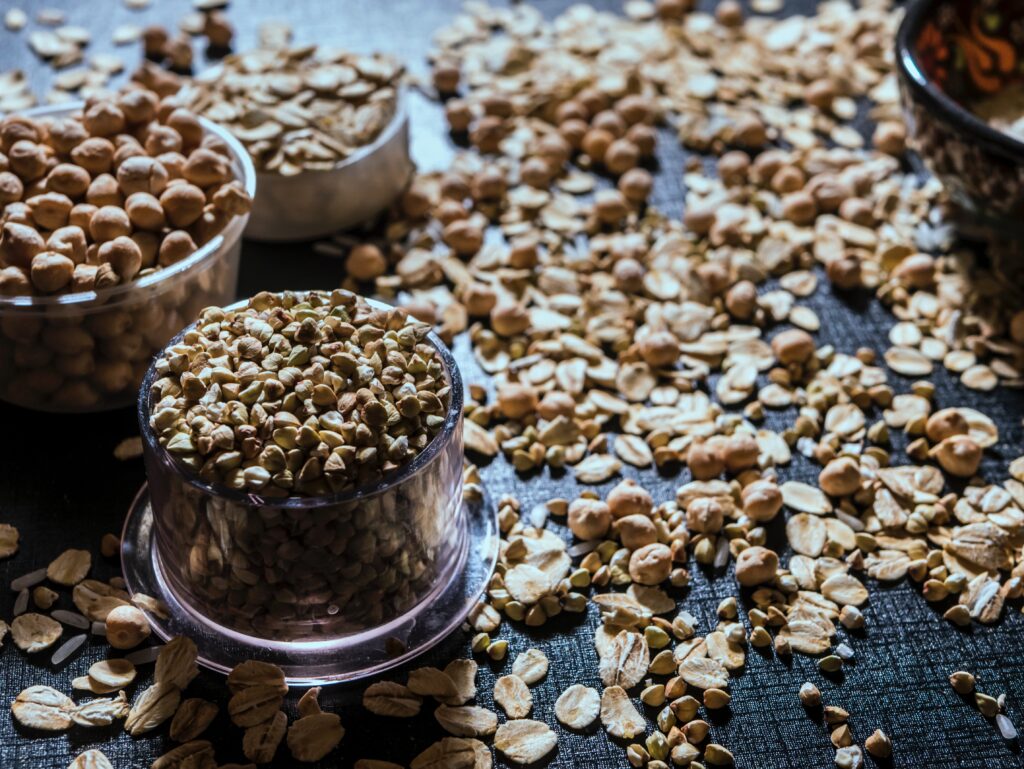

Whole Grains: Whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread are great sources of fiber, protein, and essential minerals.
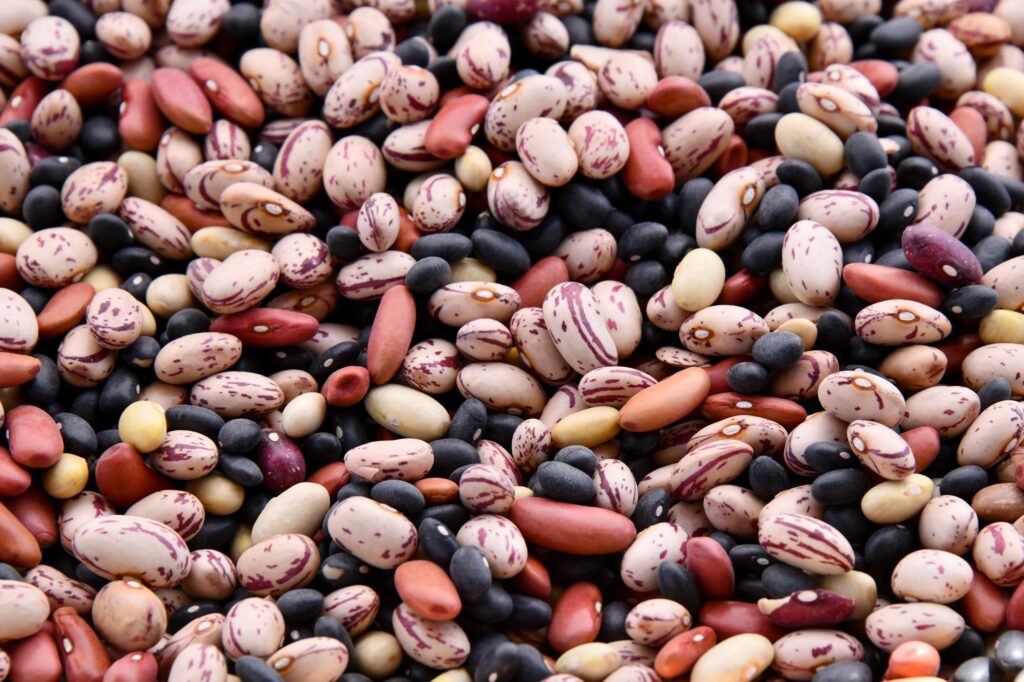

Legumes: Legumes such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas are packed with protein, fiber, and other nutrients. They can be used in a variety of recipes to add flavor and texture.
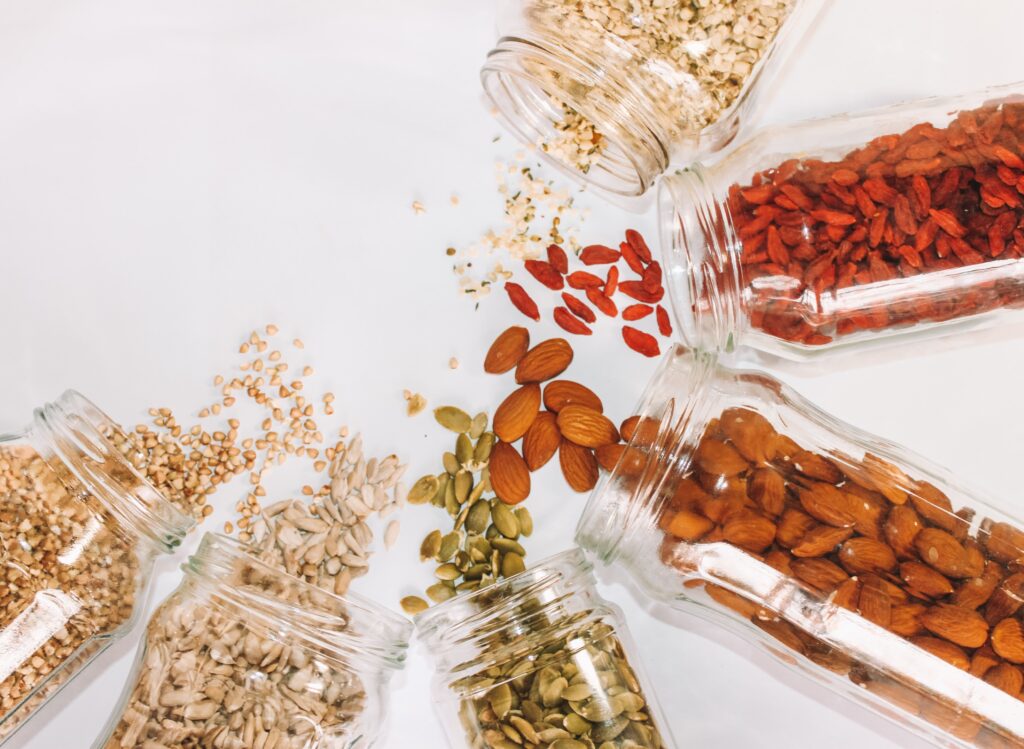

Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds are high in healthy fats, protein, and other important nutrients. They make a great snack or can be added to meals for extra nutrition.
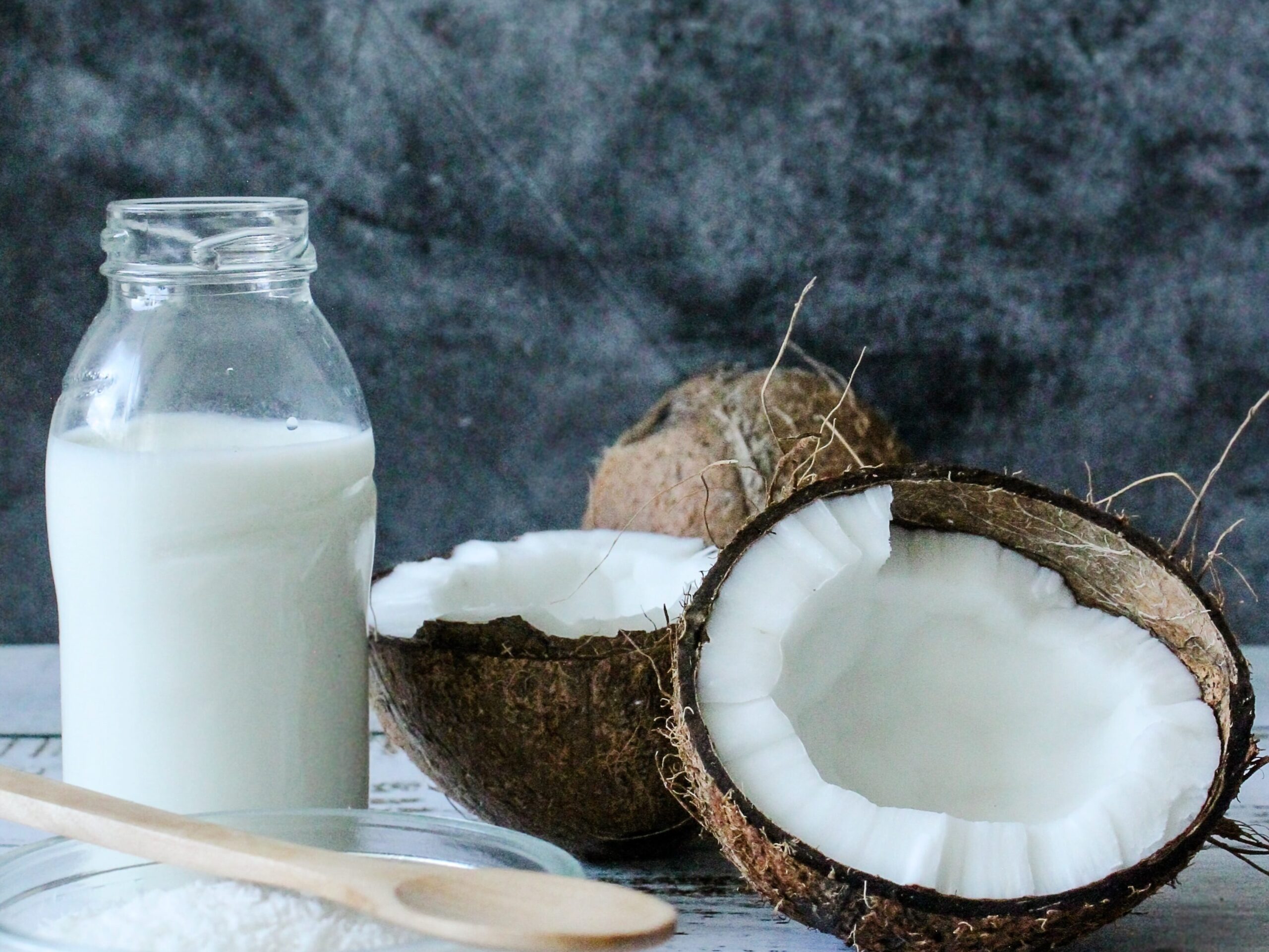

Plant-based milk and dairy alternatives: There are many plant-based milk and dairy alternatives available, including soy milk, almond milk, and coconut milk. These can be used in place of cow’s milk in recipes and can be a great addition to smoothies and cereals.
What cannot be eaten on a plant-based diet?
Meat and Poultry: This includes all forms of meat and poultry, such as beef, chicken, pork, and lamb. These foods are high in saturated fat and cholesterol, which can increase the risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions.
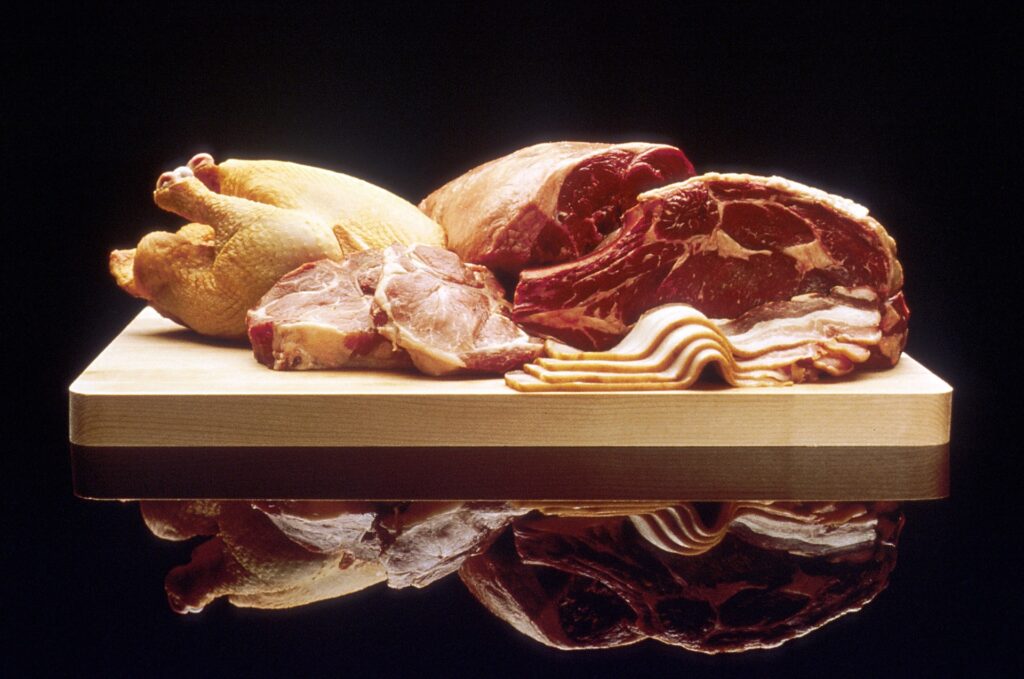
Seafood: Seafood, including fish, shellfish, and crustaceans, are also not part of a plant-based diet. These foods are high in omega-3 fatty acids and other important nutrients, but they are also often contaminated with mercury and other toxins.

Dairy Products: Dairy products, such as milk, cheese, and yogurt, are derived from animal sources and are not part of a plant-based diet. These foods are high in saturated fat and cholesterol, and can also be difficult for some people to digest.

Eggs: Eggs are not considered part of a plant-based diet because they are derived from animals. While eggs are a good source of protein and other nutrients, they are also high in cholesterol.

Honey: While honey is a natural sweetener, it is also derived from bees and is therefore not considered part of a plant-based diet. There are many other plant-based sweeteners available, such as maple syrup and agave nectar.

Most popular plant-based diet?
There are several different types of plant-based diets, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits. We will explore some of the most popular plant-based diets and what sets them apart from each other.
- Vegan Diet: A vegan diet excludes all animal products, including meat, dairy, and eggs. It emphasizes a wide variety of plant-based foods and can be a healthy way to reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Vegetarian Diet: A vegetarian diet excludes meat but may include dairy and eggs. It is also a good way to increase the intake of plant-based foods, and there are different variations such as lacto-ovo vegetarian, who consumes dairy and eggs.
- Flexitarian Diet: A flexitarian diet is a plant-based diet that allows for occasional meat consumption. This diet encourages people to eat mostly plant-based foods while still being flexible enough to include some animal products.
- Whole Food Plant-Based Diet: This diet emphasizes whole, minimally processed plant foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. It avoids highly processed foods and added sugars and can be a healthy way to reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Mediterranean Diet: While not strictly plant-based, the Mediterranean diet emphasizes plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, along with fish and small amounts of dairy and meat. This diet is known for its heart-healthy benefits and can be a good way to incorporate more plant-based foods into the diet.
By experimenting with different plant-based diets and finding what works for you, you can reap the benefits of a healthier, more sustainable diet.
What are the disadvantages of plant-based diet?
While plant-based diets have many health benefits, there are also some potential disadvantages to consider. Here are some of the main drawbacks of plant-based diets:
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Plant-based diets can be low in certain essential nutrients like vitamin B12, vitamin D, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids. While these nutrients can be obtained from plant-based sources or supplements, it’s important to pay attention to nutrient intake and potentially consult with a healthcare professional to ensure adequate nutrition.
- Digestive Issues: Plant-based diets can be high in fiber, which is great for digestion and gut health. However, some people may experience digestive issues like bloating or gas when first transitioning to a plant-based diet. Gradually increasing fiber intake and drinking plenty of water can help mitigate these issues.
- Social Challenges: Plant-based diets can be difficult to maintain in social situations where there may not be many plant-based options available. It can be challenging to navigate social events or dining out with friends and family who may not understand or support your dietary choices.
- Expense: Some plant-based foods, like fresh fruits and vegetables or specialty plant-based products, can be more expensive than animal-based foods. This can make a plant-based diet cost-prohibitive for some people.
- Misinformation: There is a lot of misinformation about plant-based diets online, and it can be difficult to navigate the conflicting advice and opinions. It’s important to do your own research and consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to ensure that you are following a healthy and balanced plant-based diet.
Overall, while there are some potential disadvantages to a plant-based diet, many of these issues can be overcome with education, planning, and support.
Who should avoid plant-based diet?
While plant-based diets can be a healthy and sustainable dietary choice for many people, there are certain individuals who may want to avoid this type of diet. Here are some groups of people who should consider alternative dietary patterns:
- People with specific nutrient deficiencies: While plant-based diets can be rich in many essential nutrients, certain nutrients such as vitamin B12 and iron are more abundant in animal-based foods. People who have difficulty meeting their nutrient needs through plant-based sources may need to consider other dietary options.
- Pregnant women: Pregnancy requires additional nutrients, including protein, iron, and calcium, which can be more challenging to obtain through a plant-based diet. Pregnant women may need to work with a healthcare professional to ensure they are meeting their nutritional needs for a healthy pregnancy.
- Athletes and highly active individuals: Athletes and individuals who engage in high levels of physical activity may require more protein and calories than can be easily obtained through a plant-based diet. Incorporating high-protein plant-based sources or considering animal-based protein sources may be necessary to meet these needs.
- People with food allergies or intolerances: Some plant-based foods can cause allergies or intolerances in certain individuals, making it difficult to consume a balanced plant-based diet.
It’s important to note that with proper planning and attention to nutrient needs, plant-based diets can be suitable for many individuals. However, those who fall into the above categories may need to consider alternative dietary options or work with a healthcare professional to ensure they are meeting their nutritional needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a plant-based diet is a healthy and sustainable way of eating that has numerous benefits for both our health and the environment. By focusing on whole, plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, we can improve our overall health and reduce our risk of chronic diseases. In addition, plant-based diets are more environmentally sustainable and can help us reduce our carbon footprint.

If you’re new to plant-based diets, don’t be intimidated! There are many delicious and satisfying plant-based meals that you can enjoy, and with a little creativity and planning, you can easily incorporate more plant-based foods into your diet. So why not give it a try? By making small changes to your diet and incorporating more plant-based foods, you can improve your health and help protect the planet.

No matter which diet you choose, it’s important to ensure that you are getting all the nutrients your body needs. This may require some planning and preparation to ensure that you are getting enough protein, iron, calcium, and other important vitamins and minerals. However, with a little bit of effort and some delicious plant-based recipes, anyone can enjoy the benefits of a plant-based diet.
Precaution!
Consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian before adopting a plant-based diet. Remember that everyone’s dietary needs are different, so find a way of eating that works for you and supports your overall health and well-being.
