Hyperloop technology is a futuristic mode of transportation that promises to revolutionize the way we travel. It is a high-speed ground transportation system that uses vacuum-sealed tubes to transport passengers and cargo at speeds of up to 760 mph (1220 km/h). Hyperloop technology was first proposed by Elon Musk, the CEO of SpaceX and Tesla, in a white paper in 2013, and since then, it has gained significant attention from investors, policymakers, and transportation experts around the world.
What is Hyperloop technology?

The Hyperloop’s core concept is to propel a pod through a tube using magnetic levitation (maglev) technology and a low-pressure environment. The tube is made of steel or concrete and is partially or completely evacuated to reduce air resistance and drag. The pod, which is essentially a capsule or a train, is propelled by electric motors and is designed to float on an air or magnet cushion. This removes the need for wheels and other moving parts, resulting in less friction and noise.
This technology offers several advantages over conventional modes of transportation, such as airplanes, trains, and cars. It is faster, safer, more energy-efficient, and less expensive to operate than other forms of transportation. It could also reduce travel time and congestion on highways and airways, allowing people to travel faster and more comfortably over long distances.
Brief history of the development of Hyperloop
The idea of high-speed ground transportation is not new, but the development of Hyperloop technology is relatively recent. In 2013, Elon Musk published a white paper titled “Hyperloop Alpha,” in which he proposed a high-speed transportation system that would connect Los Angeles and San Francisco in just 35 minutes. The proposal received widespread attention and sparked the interest of investors, engineers, and entrepreneurs.
Since then, several companies and organizations have been working on developing it, including Hyperloop Transportation Technologies (HTT), Virgin Hyperloop, and SpaceX. In 2017, Virgin Hyperloop completed the world’s first full-scale Hyperloop test in Nevada, reaching speeds of 240 mph (386 km/h). Since then, several other Hyperloop projects have been announced around the world, including routes in the United States, Europe, the Middle East, and Asia.
Advantages of Hyperloop technology
Hyperloop technology has the potential to offer several benefits over traditional modes of transportation. Here are some of the main advantages of this technology:
- High speed
Hyperloop technology is designed to operate at speeds of up to 760 mph (1220 km/h). This is much faster than any other mode of transportation currently in use, such as cars, trains, or airplanes. With this, passengers could travel long distances in a fraction of the time it would take using other modes of transportation. For example, a journey from Los Angeles to San Francisco, which currently takes around six hours by car or one hour by plane, could be completed in just 35 minutes using this technology.

- Energy efficiency
Hyperloop technology is also highly energy-efficient. The pods are powered using electricity and can be recharged using renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power. The low-pressure environment inside the tube reduces air resistance and eliminates drag, making it easier and less expensive to propel the pods. This means that it has the potential to be much more environmentally friendly than other modes of transportation.

- Low emissions
Because Hyperloop technology is powered by electricity, it emits extremely few greenhouse gases when compared to conventional modes of transportation. It does not use fossil fuels, and the low-pressure atmosphere inside the tube decreases the amount of air pollution produced while it is in operation. This makes this technology more appealing to governments and environmentalists seeking to minimize greenhouse gas emissions and battle climate change.

- Reduced travel time and congestion
Hyperloop technology has the potential to reduce travel time and congestion on highways and airways. By providing a fast and efficient mode of transportation, it could reduce the number of cars on the road and the number of flights in the air. This could help reduce traffic congestion, improve air quality, and make travel more comfortable and convenient for passengers.

- Lower cost compared to other transportation options
Finally, Hyperloop technology could be much less expensive than other modes of transportation. Because it requires less energy to operate and can be powered using renewable energy sources, it could have lower operating costs than trains, airplanes, or cars. In addition, the construction cost of a Hyperloop system could be lower than that of a high-speed rail system or a new airport. This could make it an attractive option for investors and policymakers looking for cost-effective transportation solutions.

Disadvantages of Hyperloop
While Hyperloop technology offers several potential benefits, there are also several challenges and disadvantages that need to be considered. Here are some of the main disadvantages of this technology:
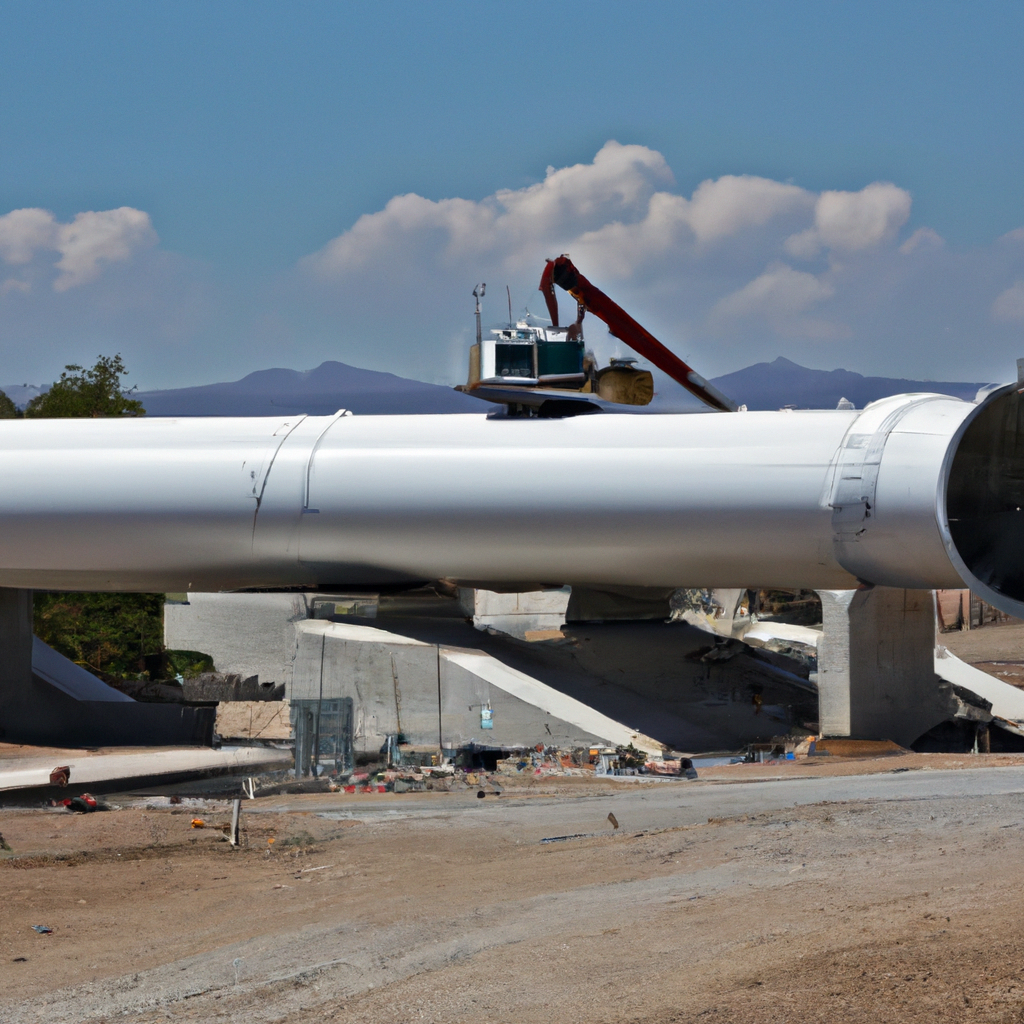

- High cost of initial construction
One of the most significant hurdles is the high initial building cost. A Hyperloop system is built by constructing a vacuum-sealed tube and installing infrastructure to sustain the transit pods. This may be an expensive and time-consuming procedure that necessitates substantial investment from both public and private sources.
- Technical challenges and uncertainties
Hyperloop technology is still in the experimental phase, and there are several technical challenges and uncertainties that need to be addressed. For example, there are concerns about the durability and safety of the tubes, the reliability of the pods, and the feasibility of maintaining a vacuum over long distances. Additionally, the technology has not yet been fully tested in real-world conditions, and there may be unforeseen challenges that arise during the development and deployment phase.

- Safety concerns
Hyperloop technology also raises safety concerns, particularly regarding the risks associated with operating at high speeds in a vacuum-sealed environment. There are concerns about the potential for accidents, such as collisions between pods or failures in the tube infrastructure, as well as the risk of decompression sickness for passengers and crew. Addressing these safety concerns will be crucial to the successful deployment of Hyperloop technology.

- Limited capacity
Another disadvantage is its limited capacity. Because the transportation pods are small and the tubes are narrow, Hyperloop systems may not be able to accommodate large numbers of passengers or cargo. This could limit the potential applications of the technology and make it less suitable for certain types of transportation, such as mass transit or shipping.
Why did Hyperloop fail?
Despite its potential benefits, it has faced several challenges and setbacks that have hindered its development and adoption. Here are some of the main reasons why some projects have failed:
- Overview of the challenges faced by further developments
The development of Hyperloop technology has been hampered by several challenges and obstacles. These include the high cost of initial construction, technical challenges and uncertainties, safety concerns, and limited capacity, which we discussed earlier in this article. Additionally, there are regulatory and legal hurdles that need to be addressed, including issues related to property rights, land use, and liability.
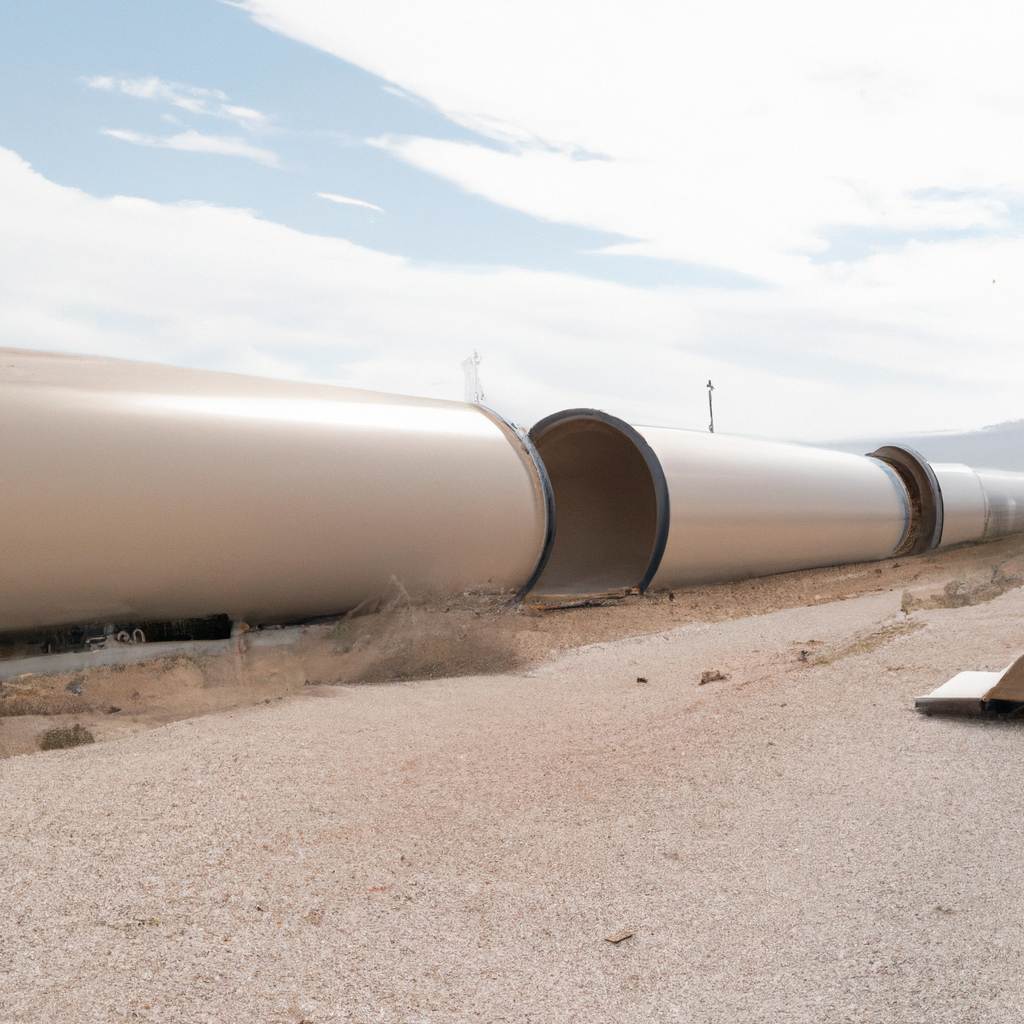

- Analysis of the reasons for the failure of some projects
Many Hyperloop projects have been planned and begun in recent years, however many have either failed to materialize or have been considerably delayed. One of the primary reasons for this is the high cost of construction, which makes it difficult for many businesses to acquire finance for their projects. Nevertheless, technological obstacles and uncertainties have made meeting the required safety and reliability criteria for Hyperloop systems challenging.
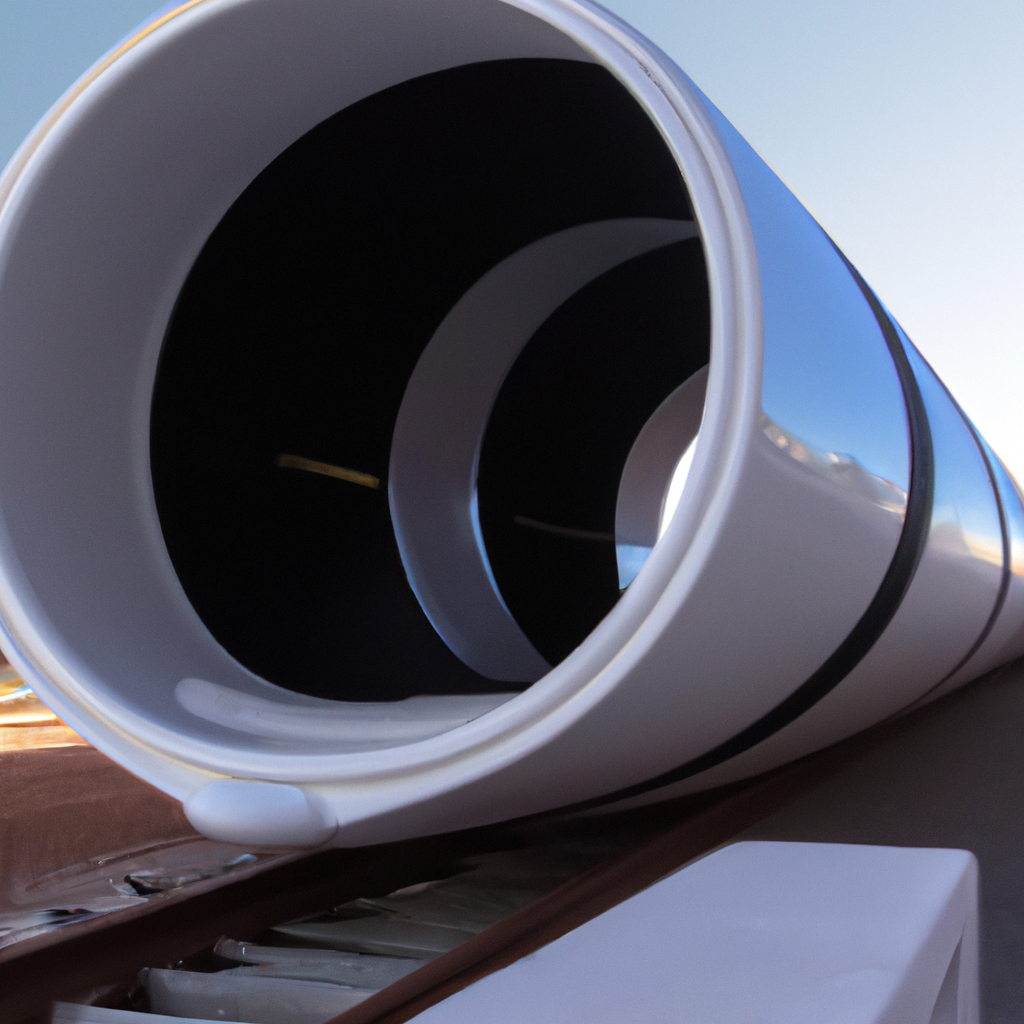

Another factor contributing to the failure of some of these projects is the lack of political and public support. Some communities have raised concerns about the potential impact of Hyperloop systems on the environment, public health, and property values. Additionally, there may be resistance from existing transportation providers, such as airlines and railways, who may view Hyperloop technology as a threat to their business models.
Finally, there is the question of whether this technology can deliver on its promised benefits, such as reduced travel times and lower costs, in practice. While there have been successful test runs of Hyperloop systems in limited settings, it remains to be seen whether the technology can be scaled up and integrated into existing transportation networks in a way that is efficient and cost-effective.
Environmental Impact of Hyperloop
In addition to the benefits and drawbacks mentioned earlier, the environmental impact of the technology is an important consideration. One of the key advantages of Hyperloop is its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants associated with transportation.
Hyperloop systems use electric propulsion and have the potential to be powered entirely by renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. This would significantly reduce the carbon footprint of transportation and help to mitigate the effects of climate change.
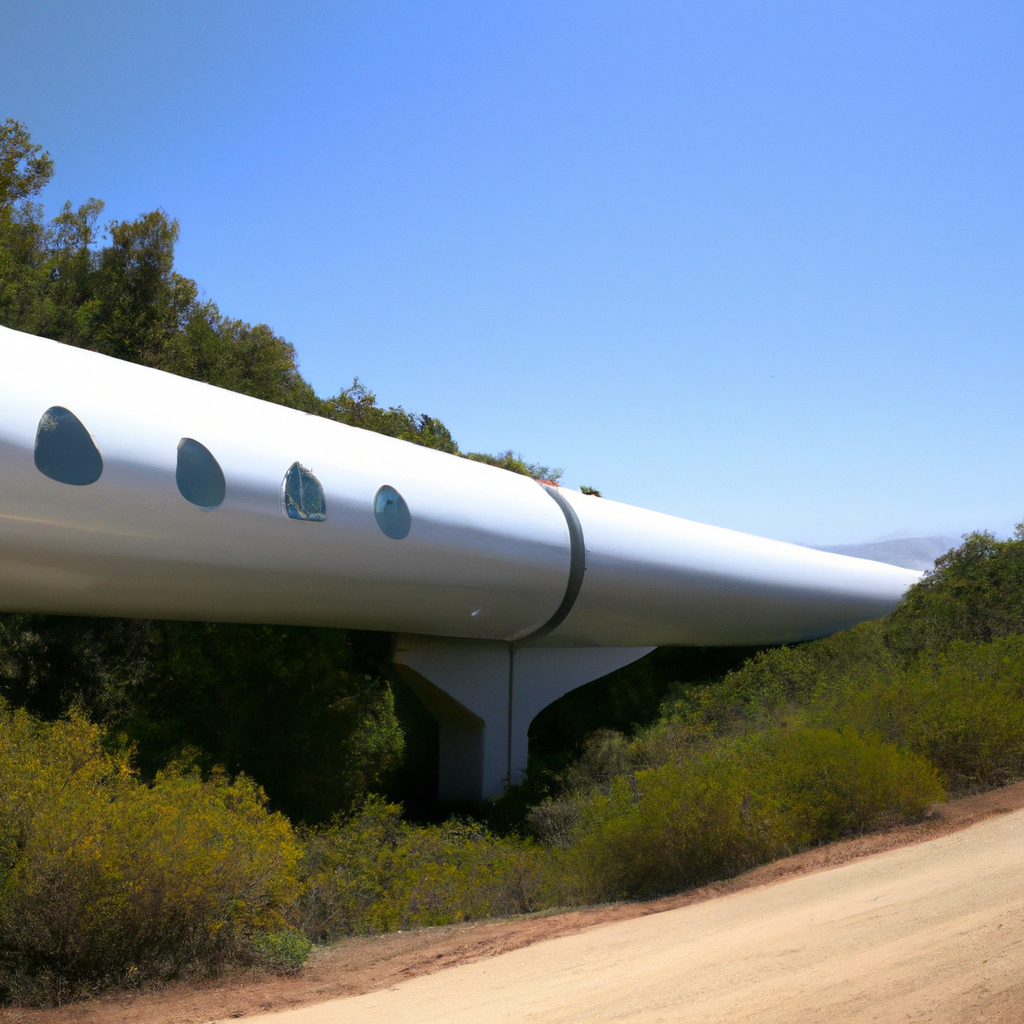

Moreover, it could help to alleviate traffic congestion and reduce the number of cars on the road, further reducing emissions and improving air quality in urban areas. The reduced travel time associated with Hyperloop could also encourage people to take more trips, leading to increased economic activity and job creation.
Overall, the environmental impact of this technology could be significant, particularly if it is developed and implemented in a sustainable manner. It has the potential to revolutionize transportation while also contributing to global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
Current status of Hyperloop development
Despite the challenges and obstacles facing the development of Hyperloop technology, there are several companies and organizations around the world that are actively pursuing Hyperloop projects. Here is an overview of some of the key players in this space and their ongoing projects:
- Overview of the companies and organizations involved in Hyperloop development
One of the most well-known companies involved in Hyperloop development is Virgin Hyperloop, which was founded in 2014 by billionaire entrepreneur Richard Branson. Virgin Hyperloop has been working on developing a high-speed transportation system that can travel at speeds of up to 1,000 km/h (620 mph). The company has successfully completed several test runs of its Hyperloop system, including a test in November 2020 that carried passengers for the first time.
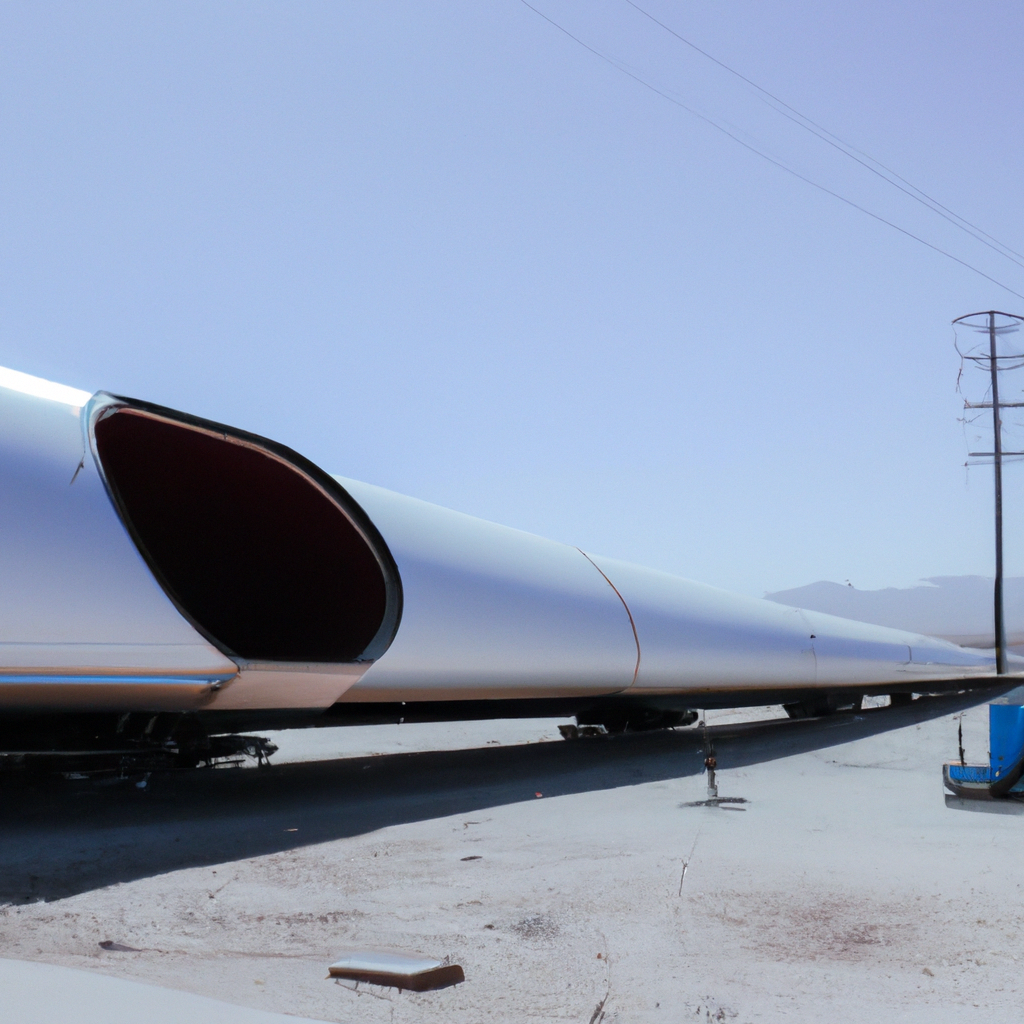

Another major player in the Hyperloop space is Hyperloop Transportation Technologies (HTT), which was founded in 2013. HTT is working on developing a Hyperloop system that uses magnetic levitation (maglev) technology to propel passenger pods through a vacuum-sealed tube. The company has partnerships with several governments and organizations around the world and has been working on several projects, including a proposed Hyperloop route between Chicago and Cleveland.
In addition to Virgin Hyperloop and HTT, there are several other companies and organizations involved in Hyperloop development, including Elon Musk’s SpaceX, which has been hosting annual Hyperloop pod competitions since 2015, and Canadian company TransPod, which is working on developing a Hyperloop system that can travel at speeds of up to 1,000 km/h (620 mph).
- Discussion of ongoing projects and their progress
Several Hyperloop projects are currently in progress around the world, with varying degrees of progress and success. One of the most advanced projects is the Virgin Hyperloop project in Saudi Arabia, which aims to connect the cities of Jeddah and Riyadh with a high-speed transportation system. The project has been granted regulatory approval and is expected to be operational by 2030.
Another project that is making progress is the proposed Hyperloop system between Mumbai and Pune in India. The project, which is being developed by Virgin Hyperloop in partnership with the government of Maharashtra, aims to reduce travel time between the two cities from three hours to just 25 minutes. The project has received regulatory approval and is currently in the planning and development stages.

Other ongoing projects include the proposed Hyperloop system between Paris and Amsterdam, which is being developed by Hardt Hyperloop, and the proposed Hyperloop system between Bratislava and Vienna, which is being developed by HyperloopTT.
ALSO READ: Latest Developments and Future of SPACE EXPLORATION
Future prospects for Hyperloop technology
Potential applications beyond passenger transportation
The future of Hyperloop technology is exciting and filled with endless possibilities. Although it is still in its infancy, there are already talks about the potential applications beyond passenger transportation. For example, it could be used to transport goods, which would significantly reduce the cost of shipping and increase the speed of delivery. This application could revolutionize the logistics industry by offering a faster and more efficient mode of transportation.

Challenges and obstacles to widespread adoption of the technology
However, various problems and roadblocks must be addressed before Hyperloop technology can be broadly implemented. The high cost of initial construction is one of the most major barriers, limiting the number of potential Hyperloop projects. Another issue is safety, as the technology has not yet been thoroughly tested and confirmed. Nevertheless, technological problems and concerns persist, notably with regard to the its capacity to operate in a variety of weather and environmental circumstances.

Possibility of integration with other transportation modes
Despite these obstacles, there is still a possibility of integrating Hyperloop technology with other transportation modes. For example, it could be used as a feeder system to connect remote regions with major cities or as a supplement to existing transportation networks. This integration could help alleviate some of the current transportation issues faced by many urban areas, such as congestion and long commute times.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the Hyperloop technology presents several advantages, including high speed, energy efficiency, low emissions, reduced travel time and congestion, and lower cost compared to other transportation options. However, it also has some significant disadvantages, such as the high cost of initial construction, technical challenges and uncertainties, safety concerns, and limited capacity.
Despite these disadvantages, the potential of this technology to transform transportation is enormous. It could significantly improve the overall travel experience for passengers and reduce the environmental impact of transportation. Moreover, it could facilitate the growth of urban areas and connect remote regions to major cities, promoting economic development.
The Hyperloop technology is still in its early stages of development, and it will take time to address the challenges and realize its full potential. However, ongoing research and development efforts have been promising, and many organizations are actively pursuing Hyperloop projects.
In conclusion, the benefits of Hyperloop technology outweigh its disadvantages, and it has the potential to revolutionize transportation. As such, it is a technology that should be taken seriously and pursued further in the coming years.
If you want to gain further knowledge about it, you can purchase the recommended book
